Table of Contents
We’ve all heard about Large Language Models (LLMs). They do amazing things like write poems or create computer code, almost like magic. These huge AI models are trained on tons of data and mostly live on the internet (in the cloud). They’ve changed what we thought AI could do. But now, something new is happening: Small Language Models (SLMs) are bringing AI directly to our devices. And for AI that works right on your phone or gadget (that’s Edge AI), these smaller models are often the better choice.
Understanding the Players: LLMs vs. SLMs
Before we dive into why SLMs are excelling on the edge, let’s quickly differentiate these two types of models.
Large Language Models (LLMs):
Size & Complexity: Think big. LLMs, like OpenAI’s GPT series or Google’s Gemini (larger versions), typically boast hundreds of billions, or even trillions, of parameters.
Training Data: They are trained on colossal, diverse datasets scraped from the internet, books, and other sources.
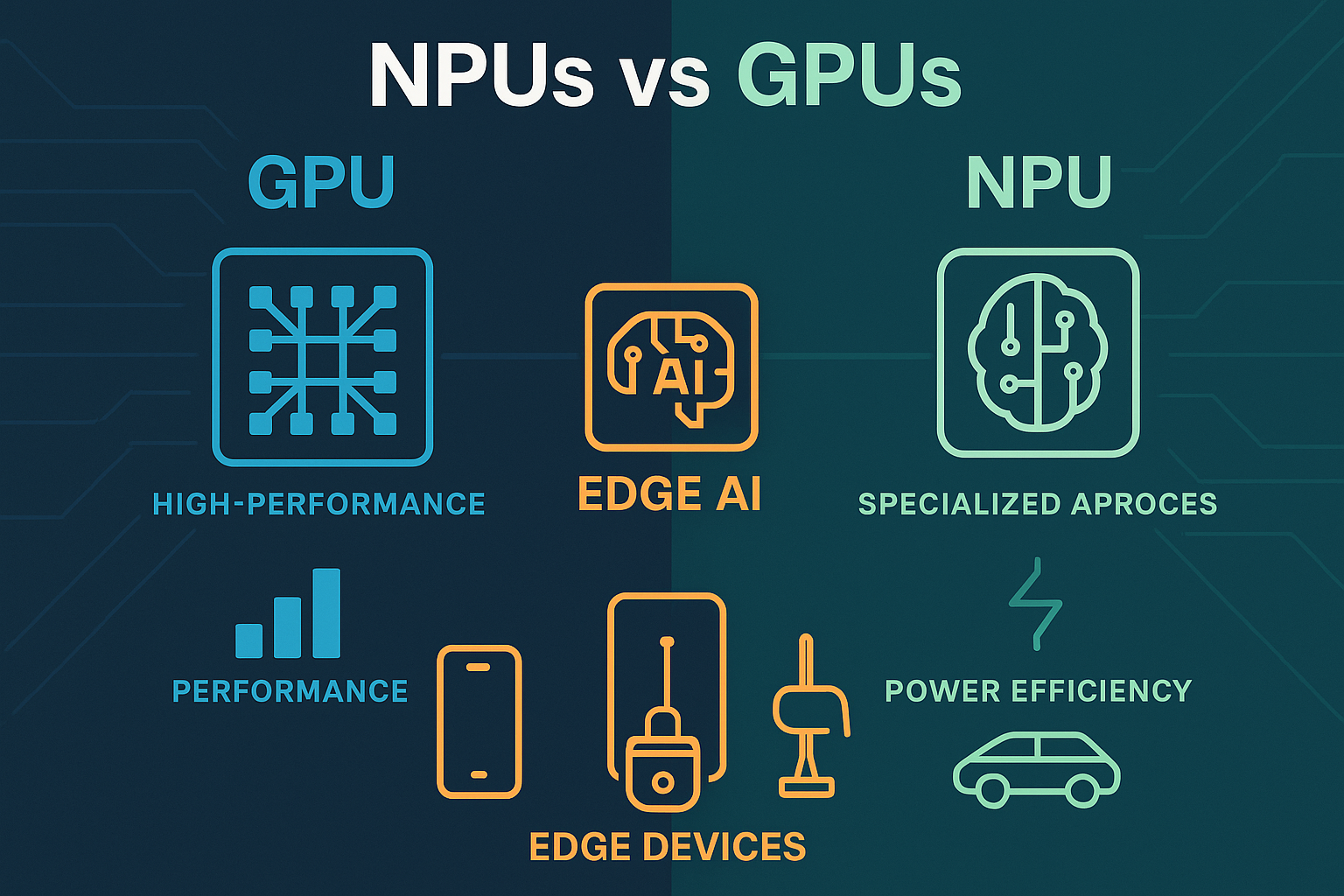
Computational Needs: Training and running LLMs require significant computational power, often involving clusters of specialized GPUs. This usually means they live in the cloud.
Generalization: Their strength lies in their ability to perform a wide array of tasks with remarkable proficiency.
Small Language Models (SLMs):
Size & Complexity: As the name suggests, SLMs are significantly smaller, with parameter counts ranging from a few million to a few billion. Examples include Microsoft’s Phi-3, Google’s Gemma (smaller variants), and models like TinyLlama.
Training Data: While still needing substantial data, SLMs can be trained on more curated or specialized datasets, making them more focused.
Computational Needs: They are designed to be more efficient, requiring less processing power and memory. This is key to their on-device capabilities.
Specialization: SLMs often excel at specific tasks or domains they are optimized for, delivering high performance within those niches.
The core trade-off is often between the broad, general-purpose intelligence of LLMs and the nimble, specialized efficiency of SLMs.
Why SLMs are Winning for Edge AI
Edge AI refers to AI computations performed locally on a user’s device (like a smartphone, wearable, or car) rather than in a centralized cloud server. This is where SLMs truly shine, enabled by powerful tools and frameworks that optimize them for on-device execution.
On-Device Processing: The Triple Threat of Privacy, Latency, and Offline Access
Privacy: With SLMs, sensitive data doesn’t need to leave your device to be processed. This is a massive win for user privacy, especially for applications handling personal information.
Low Latency: Sending data to the cloud, getting it processed, and receiving the result takes time. For applications needing real-time responses – think instant voice commands or augmented reality overlays – SLMs running locally offer significantly lower latency.
Offline Functionality: Edge AI powered by SLMs can work even without an internet connection. Imagine a translation app that works in a remote area or a smart assistant that functions during an internet outage.
Efficiency: Powering the Pocket-Sized Revolution
Edge devices are often battery-powered. SLMs, with their smaller size and optimized architecture, consume far less energy than their larger counterparts. This makes them ideal for smartphones, smartwatches, IoT sensors, and other devices where battery life is a critical concern. Crucially, the development community has produced remarkable tools to make this a reality. Frameworks like TensorFlow Lite are instrumental in this shift, providing developers the tools to convert, optimize, and deploy SLMs efficiently across a multitude of edge devices. Similarly, projects like llama.cpp are democratizing access further by enabling efficient execution of SLMs on standard CPUs, bringing powerful AI to everyday computers and a wider range of hardware without necessarily requiring specialized AI accelerators.
Cost-Effectiveness: AI for Everyone
Running LLMs in the cloud can be expensive due to the computational resources required for inference. SLMs reduce or eliminate this reliance on cloud infrastructure, leading to lower operational costs for developers and, potentially, more affordable AI-powered features for consumers.
Customization & Specialization: Tailored Intelligence
SLMs can be more easily fine-tuned or adapted for specific tasks or domains. This allows developers to create highly optimized solutions for niche applications, from medical diagnosis support on handheld devices to intelligent control systems in industrial machinery.
Speed & Responsiveness: Keeping Pace with Real Life
The reduced computational overhead of SLMs translates to faster inference times. This is crucial for applications where quick decision-making is paramount, such as driver-assistance systems in cars or interactive educational tools.
Use Cases: SLMs in Action at the Edge
The practical applications of SLMs in Edge AI are rapidly expanding, often facilitated by the aforementioned optimization tools:
Smartphones & PCs: Powering on-device assistants (like improved Siri or Google Assistant interactions), smarter predictive text, real-time language translation, email summarization, and enhanced camera features. The ability to run models on CPUs via tools like llama.cpp means even standard laptops can benefit from sophisticated local AI.
Wearables: Enabling sophisticated health monitoring, more natural voice commands on smartwatches, and personalized fitness coaching, often leveraging runtimes like TensorFlow Lite.
Automotive: Fueling in-car virtual assistants that understand natural language, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that react instantly, and personalized cabin controls.
IoT Devices: Facilitating intelligent automation in smart homes (e.g., recognizing voice commands locally), predictive maintenance in industrial settings (e.g., an SLM on a machine detecting anomalies), and smarter retail experiences, with deployment often streamlined by frameworks designed for embedded systems.
Healthcare: Supporting on-device diagnostic tools, enabling real-time analysis of medical images on portable scanners, and powering assistive technologies for individuals with disabilities.
The Future is Likely Hybrid
It’s not necessarily an “either/or” situation. The future will likely involve a hybrid approach where SLMs handle immediate, on-device tasks, while more complex queries or tasks requiring broader knowledge can be offloaded to LLMs in the cloud. This synergistic relationship will allow us to leverage the best of both worlds.
Conclusion: Smaller Models, Bigger Impact on Device Intelligence
While LLMs continue to push the boundaries of AI’s capabilities in the cloud, SLMs are spearheading a revolution in on-device intelligence. Their efficiency, speed, privacy benefits, and cost-effectiveness—bolstered by powerful software frameworks and execution environments—are making AI more accessible, responsive, and integrated into our daily lives. As SLMs become more sophisticated and easier to deploy, they are set to dominate the landscape of Edge AI, unlocking a new era of truly personal and pervasive intelligence. The “small” in SLM is proving to be a giant leap for on-device AI.





Start the conversation